ServiceNow handles user interface (UI) translations using five dedicated tables. Each table serves a different aspect of the platform’s user experience and supports internationalization (i18n) in a structured way.
1. sys_documentation
Purpose: Stores field labels (like form labels) for all languages, including English.
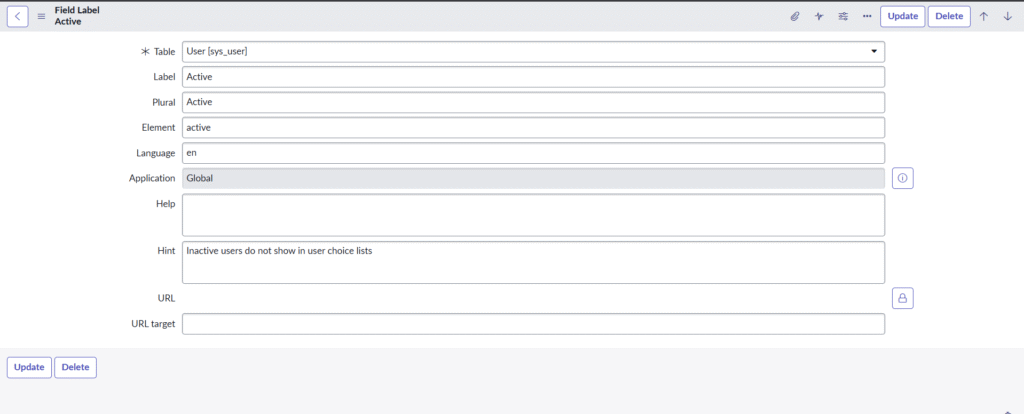
- Where it applies: Any standard or custom field label shown in the UI.
- Structure:
Table: Table name (e.g.,incident)Element: Field name (e.g.,urgency)Language: Target language (e.g.,fr)Label: Translation
- Pro tip: Always check which table the field is defined on (due to table extension) before creating a label translation.
- Update set behavior: Captured as
field labelrecords in update sets.
2. sys_choice
Purpose: Stores dropdown values (choices) like priorities, states, etc., in multiple languages.
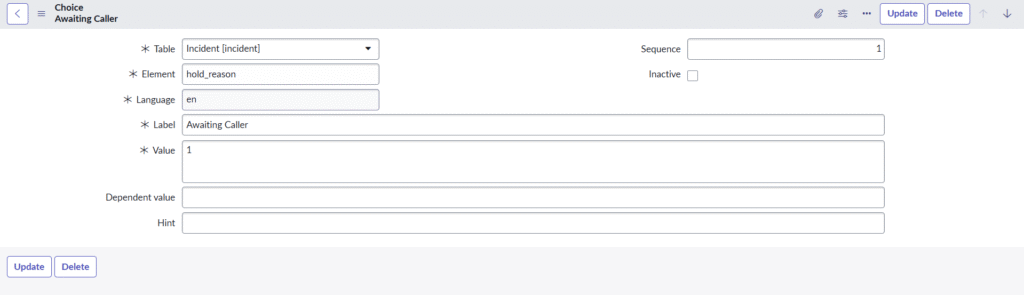
- Where it applies: Choice fields (e.g.,
priorityontasktable). - Structure:
Table,Element,LanguageValue: Backend valueLabel: What the user seesSequence: Display order
- Pro tip: Choices are case-sensitive, and you must keep values consistent across all languages to avoid logic issues.
- Update set behavior: Stored as a
Choice listin update sets.
3. sys_ui_message
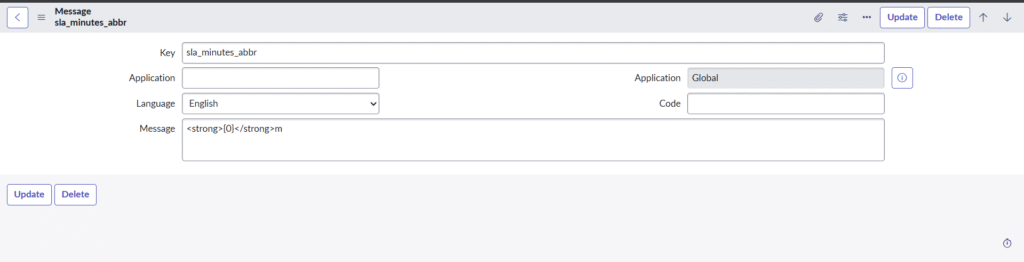
Purpose: Contains script-based messages, often used in scripts, notifications, and client/server-side logic.
- Where it applies: Messages like error messages, info messages, and confirmation prompts.
- Structure:
Key: Unique identifier (called in scripts)Language: Target languageMessage: Translated message
- Pro tip: Use
getMessage()in scripts or${}in HTML widgets to retrieve these messages. - Update set behavior: Stored as
messageentries.
4. sys_translated
Purpose: Used for fields of type translated_field (common in variables, e.g., catalog item questions).
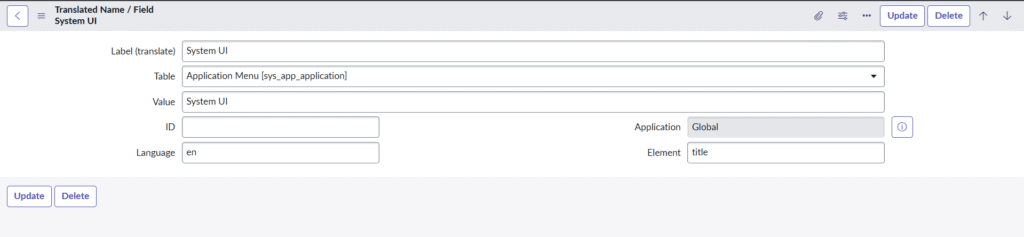
- Where it applies: Variable questions, UI policies, etc.
- Structure:
Table,Element,LanguageValue: English base valueLabel (translate): Translated value
- Pro tip: Only stores non-English translations. English is stored in the main table.
- Update set behavior: Captured as
Translated Name / Fieldrecords.
5. sys_translated_text
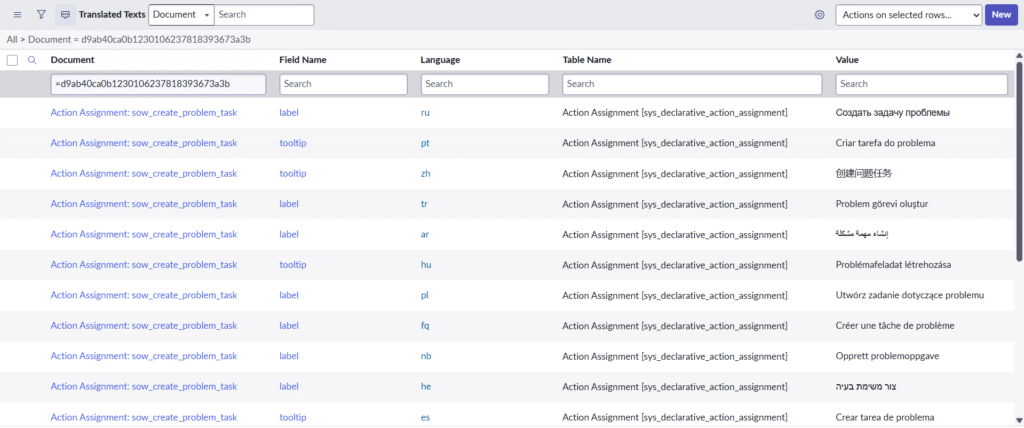
Purpose: Supports translated_text or translated_html fields, such as catalog item names or descriptions.
- Where it applies: Catalog items, Knowledge articles, etc.
- Structure:
Document: Sys ID of the source recordField Name,Language,Table Name,Value
- Pro tip: You must have the serializer attribute set properly on the field; otherwise, translations won’t load.
- Update set behavior: Stored inside the XML of the original record, not separately.
🔧 Best Practices for Working with Translations
- Use the Localization Framework for structured translation workflows (especially for portal, workspace, VA topics).
- Avoid manual spreadsheet imports unless necessary; they’re prone to errors and often not upgrade-safe.
- If you must use spreadsheets:
- Export records from these tables
- Coalesce on key fields to avoid duplicates
- Reimport translations carefully
- Keep translations in lower environments, then migrate using update sets to avoid loss during upgrades.
⚠️ Common Pitfalls
- ❌ Modifying OOTB translations directly in production
- ❌ Forgetting to set proper field types (
translated_text) - ❌ Missing the
serializerattribute on translated fields - ❌ Using inconsistent values in
sys_choiceacross languages
✅ Summary Table
| Table | Type of Translation | Includes English? | In Update Sets? |
|---|---|---|---|
sys_documentation | Field Labels | ✅ Yes | ✅ As Field Label |
sys_choice | Dropdown (Choice) Values | ✅ Yes | ✅ As Choice List |
sys_ui_message | Scripted / UI Messages | ✅ Yes | ✅ As Message |
sys_translated | Translated Field Values | ❌ No | ✅ Translated Field |
sys_translated_text | Translated Text/HTML Fields | ❌ No | ✅ In Record XML |

